Blockchain technology, originally known for its application in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, has gained significant attention in recent years for its potential to revolutionize various industries, including healthcare. By offering a decentralized and immutable ledger system, blockchain holds the promise of enhancing data security, interoperability, and transparency in healthcare, ultimately improving patient outcomes and streamlining administrative processes. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the transformative impact of blockchain technology on healthcare, examining its applications, benefits, challenges, and future directions.
 Understanding Blockchain Technology: Principles and Concepts
Understanding Blockchain Technology: Principles and Concepts
At its core, blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that enables secure, transparent, and tamper-resistant recording of transactions across a network of interconnected nodes. Key principles of blockchain technology include:
Decentralization: Blockchain operates on a decentralized network of nodes, eliminating the need for a central authority or intermediary to validate transactions. Each node maintains a copy of the entire blockchain ledger, ensuring redundancy, fault tolerance, and data resilience.
Immutability: Once recorded, data stored on the blockchain cannot be altered, tampered with, or deleted without consensus from the majority of network participants. This immutability feature ensures data integrity, auditability, and trustworthiness, making blockchain an ideal platform for recording sensitive transactions and maintaining an indisputable record of events.
Cryptographic Security: Blockchain employs cryptographic techniques, such as public-key cryptography and digital signatures, to secure transactions, authenticate users, and protect data privacy. Encryption algorithms ensure that sensitive information remains confidential, while cryptographic hashes provide a unique fingerprint for each block, enabling verification of data integrity and authenticity.
 Applications of Blockchain in Healthcare: Enhancing Data Security and Interoperability
Applications of Blockchain in Healthcare: Enhancing Data Security and Interoperability
Blockchain technology has diverse applications across various domains of healthcare, offering solutions to longstanding challenges related to data security, interoperability, and information exchange. Key applications include:
Secure Health Data Exchange: Blockchain facilitates secure and interoperable exchange of health data among disparate healthcare systems, providers, and stakeholders. By creating a decentralized network for data sharing and access control, blockchain enables patients to maintain ownership and control over their health records while granting permission to authorized entities for data sharing and treatment coordination.
Health Information Management: Blockchain streamlines health information management processes, such as patient identity verification, medical record retrieval, and consent management. Smart contracts, self-sovereign identity solutions, and decentralized identity platforms enable patients to securely access, share, and manage their health information across different healthcare providers and settings.
Supply Chain Management: Blockchain enhances transparency and traceability in pharmaceutical supply chains by recording the entire lifecycle of pharmaceutical products, from manufacturing and distribution to patient administration. Blockchain-based supply chain solutions enable real-time tracking of drug shipments, verification of product authenticity, and detection of counterfeit medications, reducing the risk of medication errors and ensuring patient safety.
How To Prevent Cavities Naturally: EFFECTIVE STRATEGIES [2024]
NEW: Cosmetic Dentistry Insurance, What’s In and What’s Out, Important background Information[2024]
The Luxury Toothpaste Trend: Worth the Price Tag? (2024 INSIGHTS)
Hidden Costs of Oral Health Neglect and How to Avoid Them (2024)
Benefits of Blockchain Technology in Healthcare: Improving Patient Outcomes and Administrative Efficiency
Blockchain technology offers a myriad of benefits for patients, healthcare providers, and healthcare organizations, including:
Enhanced Data Security: Blockchain provides robust data security measures, including encryption, cryptographic hashing, and decentralized consensus mechanisms, to protect sensitive health information from unauthorized access, tampering, and data breaches. By ensuring data integrity and confidentiality, blockchain enhances patient privacy and mitigates cybersecurity risks in healthcare.
Interoperability and Data Exchange: Blockchain facilitates seamless interoperability and data exchange among different healthcare systems, electronic health record (EHR) platforms, and medical devices, enabling real-time access to comprehensive patient information and promoting care coordination across care settings. Interoperable blockchain networks improve care delivery, reduce duplicate testing, and enhance care quality and safety.
Streamlined Administrative Processes: Blockchain simplifies administrative processes, such as claims processing, billing reconciliation, and provider credentialing, by automating workflow tasks, reducing administrative overhead, and minimizing errors and discrepancies. Smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps) enable self-executing agreements and automated transactions, accelerating administrative workflows and reducing administrative costs for healthcare organizations.
 Challenges and Considerations in Blockchain Implementation in Healthcare
Challenges and Considerations in Blockchain Implementation in Healthcare
Despite its potential benefits, blockchain technology faces several challenges and considerations that must be addressed to realize its full potential and scalability in healthcare. Key challenges include:
Regulatory Uncertainty: Blockchain implementation in healthcare is subject to regulatory frameworks, privacy regulations, and data protection laws, which vary across jurisdictions and may pose barriers to adoption and compliance. Regulatory uncertainty regarding data ownership, consent management, and liability issues requires clarity and guidance from policymakers and regulatory authorities to foster innovation and ensure regulatory compliance in blockchain-based healthcare solutions.
Data Privacy and Confidentiality: Blockchain raises concerns about data privacy, confidentiality, and compliance with healthcare privacy regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States. While blockchain offers cryptographic security measures to protect health data, ensuring patient consent, data minimization, and granular access controls are essential for maintaining patient trust and regulatory compliance in blockchain-based healthcare systems.
Scalability and Performance: Blockchain scalability and performance limitations, including transaction throughput, network latency, and storage capacity, may hinder the adoption and scalability of blockchain-based healthcare solutions, particularly in large-scale healthcare networks and high-volume transaction environments. Scalability solutions, such as off-chain transactions, sharding, and layer-2 protocols, are being explored to address scalability challenges and enhance the efficiency and throughput of blockchain networks in healthcare.
Future Directions: Innovations and Opportunities in Blockchain-Based Healthcare
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, several emerging trends and innovations hold promise for advancing the field and addressing existing challenges. Key areas of focus include:
Interoperable Blockchain Networks: Interoperable blockchain networks enable seamless data exchange and interoperability among disparate healthcare systems, EHR platforms, and medical devices, fostering care coordination, data liquidity, and information exchange across care settings. Standardized protocols, interoperability frameworks, and open-source platforms facilitate integration and interoperability among blockchain-based healthcare systems and existing health IT infrastructure.
Blockchain-Enabled Healthcare Marketplaces: Blockchain-based healthcare marketplaces and decentralized platforms empower patients to securely access, share, and monetize their health data while maintaining control over their personal health information. Patient-centric data marketplaces enable individuals to participate in research studies, clinical trials, and health data monetization initiatives, contributing to medical research, precision medicine, and healthcare innovation while preserving patient privacy and data ownership rights.
Tokenization and Incentive Mechanisms: Tokenization and incentive mechanisms leverage blockchain-based tokens, cryptocurrencies, and digital assets to incentivize participation, reward value creation, and promote engagement in healthcare ecosystems. Token-based incentive models, such as tokenized rewards, staking mechanisms, and decentralized governance structures, encourage data sharing, collaborative research, and community-driven innovation in healthcare, aligning incentives among stakeholders and fostering a culture of innovation and collaboration in healthcare.
Blockchain technology holds immense promise for transforming healthcare by enhancing data security, interoperability, and transparency across healthcare systems and stakeholders. By leveraging blockchain’s decentralized ledger system, cryptographic security, and smart contract functionality, healthcare organizations can streamline administrative processes, improve data exchange, and enhance patient outcomes while ensuring data privacy, confidentiality, and regulatory compliance. As we navigate the complexities of blockchain implementation in healthcare, it is essential to address regulatory, technical, and ethical considerations while embracing innovations that advance the field and promote equitable access to high-quality healthcare for all individuals. With continued collaboration, innovation, and commitment to patient-centered care, blockchain has the potential to revolutionize healthcare delivery and drive positive change in the healthcare industry.
 Today is the last day of the 2023-2024 Champions League semi final games. Real Madrid will be hosting Bayern Munich today, 8th May 2024, at the Santiago Bernabèu for the return leg of the tie which ended in a stalemate in the first leg. Incase you are looking for how to stream Real Madrid Vs Bayern for free, then you are at the right place.
Today is the last day of the 2023-2024 Champions League semi final games. Real Madrid will be hosting Bayern Munich today, 8th May 2024, at the Santiago Bernabèu for the return leg of the tie which ended in a stalemate in the first leg. Incase you are looking for how to stream Real Madrid Vs Bayern for free, then you are at the right place.
 Introduction:
Introduction: 2. Key Trends Shaping the African Insurance Market:
2. Key Trends Shaping the African Insurance Market: 5. Strategies for Enhancing Insurance Penetration:
5. Strategies for Enhancing Insurance Penetration: In the bustling landscape of modern life, where demands on time and attention seem endless, prioritizing fitness often takes a backseat. Yet, amidst the chaos, the importance of physical activity and well-being cannot be overstated. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve deep into the multifaceted world of fitness, uncovering its profound impact on body, mind, and spirit. From the physiological benefits of exercise to the psychological effects of movement, we uncover the transformative power of fitness in shaping a vibrant and balanced life.
In the bustling landscape of modern life, where demands on time and attention seem endless, prioritizing fitness often takes a backseat. Yet, amidst the chaos, the importance of physical activity and well-being cannot be overstated. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve deep into the multifaceted world of fitness, uncovering its profound impact on body, mind, and spirit. From the physiological benefits of exercise to the psychological effects of movement, we uncover the transformative power of fitness in shaping a vibrant and balanced life. The Psychological Impact of Exercise:
The Psychological Impact of Exercise: The Social Dimension of Fitness:
The Social Dimension of Fitness:
 Understanding Teletherapy: A New Frontier in Mental Health Care
Understanding Teletherapy: A New Frontier in Mental Health Care Applications of Teletherapy in Mental Health Care
Applications of Teletherapy in Mental Health Care Advantages of Teletherapy: Improving Access and Engagement
Advantages of Teletherapy: Improving Access and Engagement Future Directions: Innovations and Opportunities in Teletherapy
Future Directions: Innovations and Opportunities in Teletherapy Understanding Blockchain Technology: Principles and Concepts
Understanding Blockchain Technology: Principles and Concepts Applications of Blockchain in Healthcare: Enhancing Data Security and Interoperability
Applications of Blockchain in Healthcare: Enhancing Data Security and Interoperability Challenges and Considerations in Blockchain Implementation in Healthcare
Challenges and Considerations in Blockchain Implementation in Healthcare Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) has emerged as a critical component of modern healthcare delivery, enabling healthcare providers to monitor patients’ health status, vital signs, and disease progression outside of traditional clinical settings. By leveraging digital health technologies, wearable devices, and telecommunication platforms, RPM facilitates real-time data collection, remote surveillance, and proactive interventions, empowering patients to manage chronic conditions, prevent complications, and achieve better health outcomes. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the transformative potential of RPM, examining its applications, benefits, challenges, and future directions in reshaping the healthcare landscape.
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) has emerged as a critical component of modern healthcare delivery, enabling healthcare providers to monitor patients’ health status, vital signs, and disease progression outside of traditional clinical settings. By leveraging digital health technologies, wearable devices, and telecommunication platforms, RPM facilitates real-time data collection, remote surveillance, and proactive interventions, empowering patients to manage chronic conditions, prevent complications, and achieve better health outcomes. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the transformative potential of RPM, examining its applications, benefits, challenges, and future directions in reshaping the healthcare landscape. The Evolution of Remote Patient Monitoring: From Passive to Active Care
The Evolution of Remote Patient Monitoring: From Passive to Active Care
 Challenges and Considerations in Remote Patient Monitoring Implementation
Challenges and Considerations in Remote Patient Monitoring Implementation Remote patient monitoring represents a paradigm shift in healthcare delivery, offering a transformative approach to patient care that extends beyond the confines of traditional clinical settings. By harnessing the power of digital health technologies, wearable sensors, and telecommunication platforms, remote patient monitoring enables proactive management of chronic conditions, seamless transitions of care, and enhanced patient engagement in their healthcare journey. As we navigate the evolving landscape of remote patient monitoring, it is essential to address technological, regulatory, and ethical challenges while embracing innovations that advance the field and promote equitable access to high-quality healthcare for all individuals. With continued innovation, collaboration, and commitment to patient-centered care, remote patient monitoring holds the promise of revolutionizing healthcare delivery and improving outcomes for patients worldwide.
Remote patient monitoring represents a paradigm shift in healthcare delivery, offering a transformative approach to patient care that extends beyond the confines of traditional clinical settings. By harnessing the power of digital health technologies, wearable sensors, and telecommunication platforms, remote patient monitoring enables proactive management of chronic conditions, seamless transitions of care, and enhanced patient engagement in their healthcare journey. As we navigate the evolving landscape of remote patient monitoring, it is essential to address technological, regulatory, and ethical challenges while embracing innovations that advance the field and promote equitable access to high-quality healthcare for all individuals. With continued innovation, collaboration, and commitment to patient-centered care, remote patient monitoring holds the promise of revolutionizing healthcare delivery and improving outcomes for patients worldwide. Principles of Personalized Medicine: From One-Size-Fits-All to Targeted Therapies
Principles of Personalized Medicine: From One-Size-Fits-All to Targeted Therapies Applications of Personalized Medicine: From Oncology to Preventive Health
Applications of Personalized Medicine: From Oncology to Preventive Health In an era defined by technological innovation and interconnectedness, telemedicine has emerged as a transformative force in healthcare delivery, offering new avenues for remote consultation, diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring. With advancements in digital communication, mobile technology, and virtual care platforms, telemedicine has the potential to expand access to healthcare services, improve patient outcomes, and enhance the efficiency of healthcare delivery systems. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the multifaceted realm of telemedicine, examining its evolution, applications, benefits, challenges, and future directions.
In an era defined by technological innovation and interconnectedness, telemedicine has emerged as a transformative force in healthcare delivery, offering new avenues for remote consultation, diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring. With advancements in digital communication, mobile technology, and virtual care platforms, telemedicine has the potential to expand access to healthcare services, improve patient outcomes, and enhance the efficiency of healthcare delivery systems. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the multifaceted realm of telemedicine, examining its evolution, applications, benefits, challenges, and future directions. Applications of Telemedicine in Healthcare
Applications of Telemedicine in Healthcare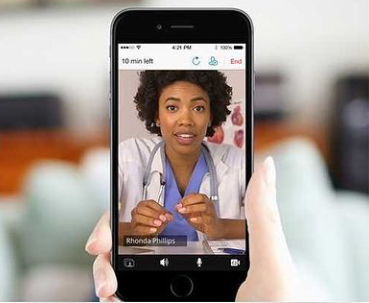
 Future Directions: Innovations and Opportunities in Telemedicine
Future Directions: Innovations and Opportunities in Telemedicine Unleashing the Power of Data: AI Applications in Healthcare
Unleashing the Power of Data: AI Applications in Healthcare Challenges and Opportunities: Navigating the AI Landscape in Healthcare
Challenges and Opportunities: Navigating the AI Landscape in Healthcare Future Directions: Innovations and Challenges on the Horizon
Future Directions: Innovations and Challenges on the Horizon In recent years, the United States has been gripped by a devastating epidemic of opioid misuse, addiction, and overdose deaths. This complex public health crisis has exacted a profound toll on individuals, families, and communities across the nation, highlighting the urgent need for comprehensive strategies to combat opioid misuse and prevent further harm. In this comprehensive examination, we delve into the multifaceted dimensions of the opioid epidemic, exploring its origins, impacts, and potential solutions to mitigate its devastating effects.
In recent years, the United States has been gripped by a devastating epidemic of opioid misuse, addiction, and overdose deaths. This complex public health crisis has exacted a profound toll on individuals, families, and communities across the nation, highlighting the urgent need for comprehensive strategies to combat opioid misuse and prevent further harm. In this comprehensive examination, we delve into the multifaceted dimensions of the opioid epidemic, exploring its origins, impacts, and potential solutions to mitigate its devastating effects.